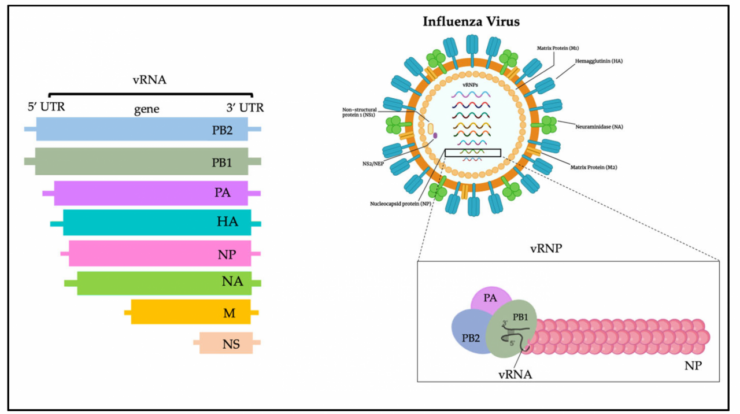
The H5N1 pandemic, a highly pathogenic avian influenza virus, has emerged as a global health concern. Its potential for human transmission and severe illness has raised alarms, prompting urgent research and public health interventions.
This virus, with its unique characteristics and zoonotic potential, poses significant challenges to diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. Understanding the epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and public health response to the H5N1 pandemic is crucial for mitigating its impact and preparing for future outbreaks.
Epidemiology of H5N1 Pandemic
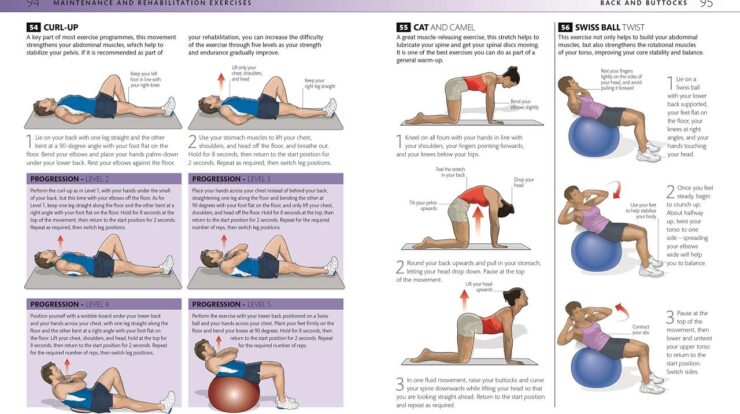
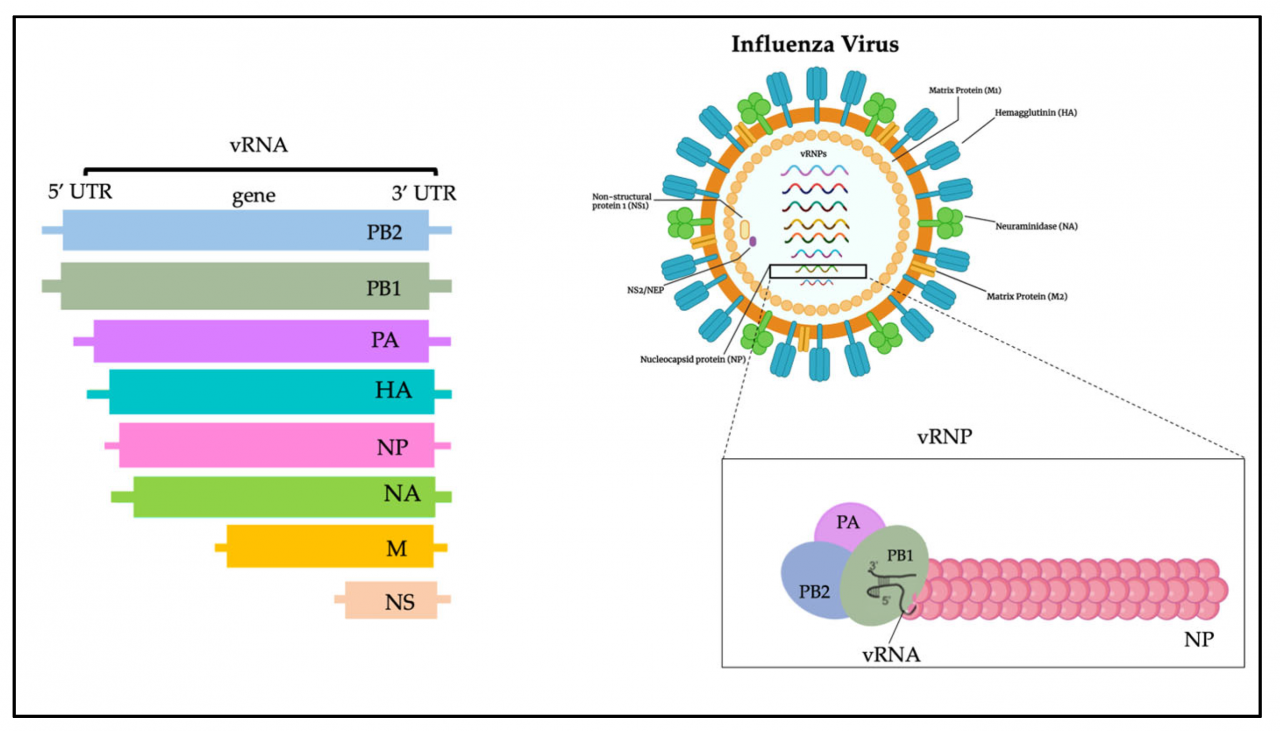
The H5N1 influenza pandemic emerged in 1997 and has since become a global concern. It is a highly pathogenic avian influenza virus that has caused outbreaks in poultry and sporadic infections in humans.
The virus has a wide geographic distribution, with outbreaks reported in Asia, Europe, Africa, and North America. Transmission primarily occurs through contact with infected poultry or their secretions.
Characteristics of H5N1 Virus
- Highly pathogenic in poultry, causing severe respiratory disease and high mortality rates.
- Can mutate and acquire new virulence factors, increasing its transmissibility and pathogenicity.
- Has a high potential for zoonotic transmission, with humans infected through contact with infected birds or contaminated environments.
Role of Animal Reservoirs
Wild birds, particularly waterfowl, serve as natural reservoirs for H5N1 virus. The virus can persist in these birds without causing clinical disease, but it can be transmitted to domestic poultry and humans.
Clinical Manifestations and Diagnosis
Clinical Manifestations
- Respiratory symptoms: fever, cough, shortness of breath, sore throat.
- Systemic complications: pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), multi-organ failure.
- High mortality rates, especially in severe cases.
Diagnostic Methods
- Laboratory testing: Real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) to detect viral RNA in respiratory samples.
- Imaging techniques: Chest X-ray or computed tomography (CT) scans to visualize lung abnormalities.
Challenges and Limitations
Diagnosing H5N1 infection can be challenging due to its non-specific symptoms and the need for specialized laboratory tests.
Treatment and Prevention
Treatment Options
- Antiviral medications: Oseltamivir and zanamivir are effective in reducing viral replication and improving outcomes.
- Supportive care: Oxygen therapy, mechanical ventilation, and intensive care management for severe cases.
Role of Vaccination
Vaccines are available to prevent H5N1 infection in poultry and humans. However, their effectiveness against new or mutated strains may vary.
Challenges and Limitations
Treatment options for H5N1 infection are limited, and antiviral resistance is a concern. Vaccination programs face challenges in terms of cost, logistics, and vaccine efficacy.
Public Health Response: H5n1 Pandemic
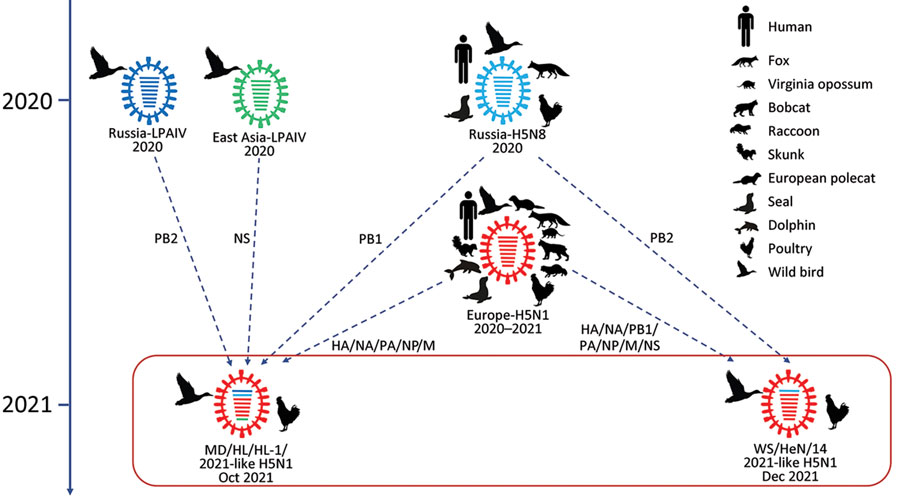
Public Health Measures, H5n1 pandemic
- Surveillance: Monitoring for outbreaks in poultry and humans.
- Containment: Culling infected poultry and isolating infected individuals.
- Mitigation: Promoting good hygiene practices, travel restrictions, and public awareness campaigns.
Challenges and Limitations
Public health responses to H5N1 pandemic have faced challenges such as inadequate surveillance systems, delayed reporting, and resistance to control measures.
Lessons Learned
The H5N1 pandemic has highlighted the need for improved surveillance, early detection, and rapid response mechanisms for future pandemic preparedness.
Economic and Societal Impacts
Economic Impacts
- Disruptions to poultry industry, leading to losses in production and trade.
- Travel restrictions and quarantine measures, affecting tourism and business activities.
Societal Impacts
- Psychological and emotional distress due to fear of infection and social isolation.
- Disruptions to daily life, including school closures and cancellation of public events.
Role of Media and Social Media
The media and social media play a crucial role in shaping public perception of H5N1 pandemic, both positively and negatively.
Last Word
The H5N1 pandemic serves as a reminder of the ongoing threat of emerging infectious diseases and the need for continued surveillance, research, and international collaboration. Lessons learned from this pandemic will inform pandemic preparedness and response efforts, ensuring a more effective and coordinated global response to future health crises.